-
Understanding Solar Inverter Technologies
Solar power systems utilize various inverter technologies to transform the energy generated by solar panels into usable electricity. The choice of inverter plays a crucial role in system performance, efficiency, and adaptability to different conditions. Here’s an overview of three main types of solar inverters:
String Inverters: Traditional and Reliable
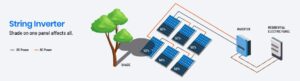
How They Work: String inverters are a conventional choice, connecting multiple solar panels in a series or “string.” These inverters convert DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity suitable for household use or grid feeding.
Advantages: String inverters are cost-effective and well-established in solar installations. They’re ideal when panels face the same direction without shading concerns.
Disadvantages: The performance of the entire string can be compromised if one panel underperforms due to shading or dirt. They might have lower efficiency compared to other options.
String Inverters with Power Optimizers: Enhanced Efficiency
How They Work: This technology combines string inverters with power optimizers attached to each panel. Optimizers maximize energy harvest per panel, overcoming shading or performance issues affecting individual panels.
Advantages: Power optimizers countershading, soiling, or mismatch, optimizing system performance. They enable panel-level monitoring for performance tracking.
Disadvantages: Though more efficient than traditional string inverters, this option can be pricier due to added hardware.
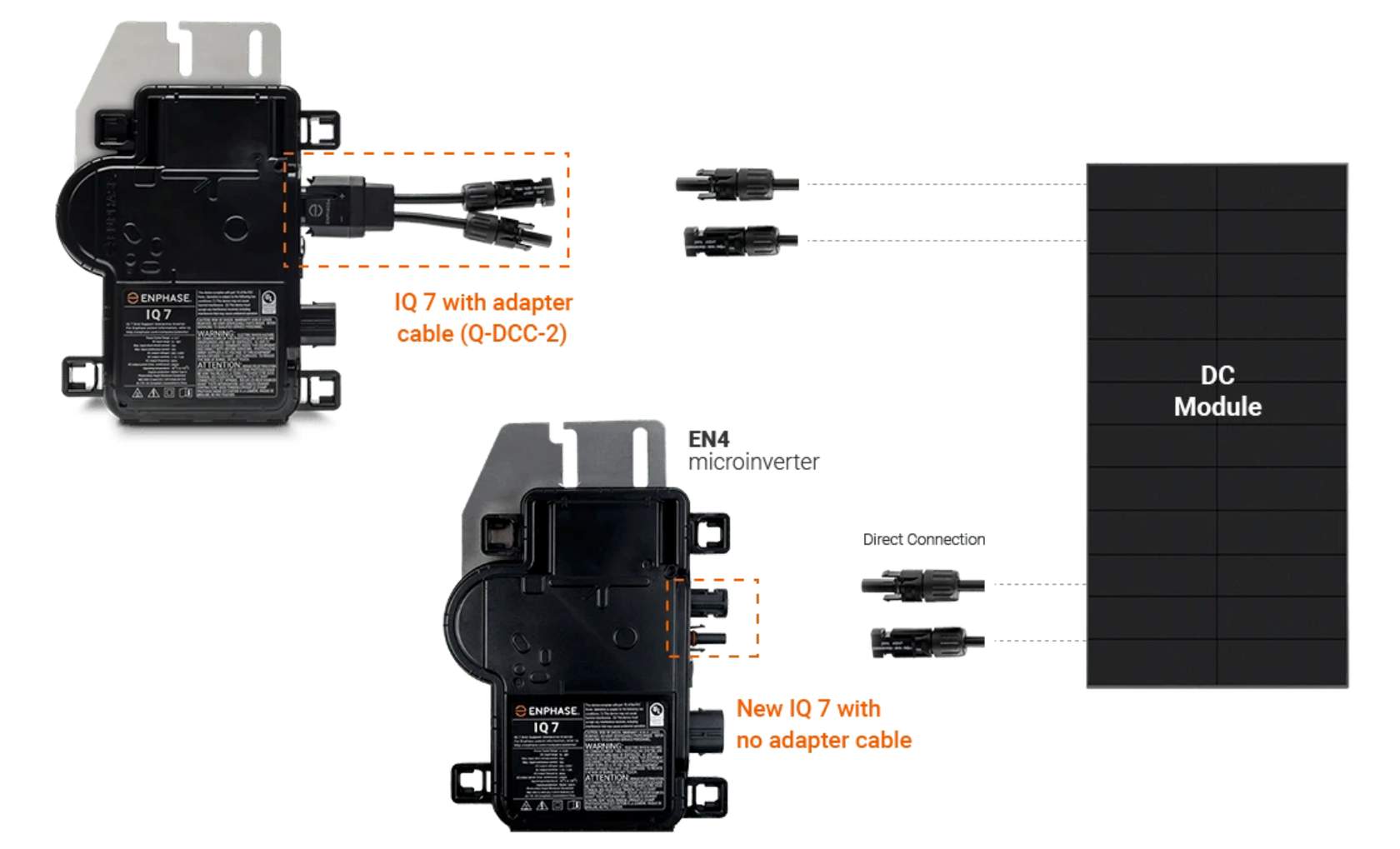
Microinverters: Panel-Level Precision
How They Work: Microinverters are mounted directly on each solar panel, converting DC to AC at the panel level. Unlike string inverters, they eliminate the need for a central inverter, allowing each panel to operate independently.
Advantages: Microinverters excel in shading or varying orientation scenarios, providing high efficiency. Individual panel monitoring simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting.
Disadvantages: Microinverters can be more costly and installation might be more intricate due to individual mounting.
Making the Right Choice
The inverter you select hinges on factors like budget, panel arrangement, shading, and monitoring needs. Engaging a solar professional to assess your specific requirements ensures you make an informed decision that aligns with your preferences.
Microinverters: Precision and Efficiency
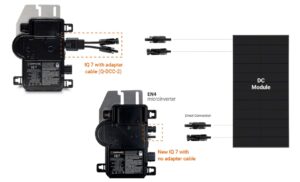
Microinverters are affixed directly to each solar panel within an array, converting DC power into AC power right at the back of each panel.
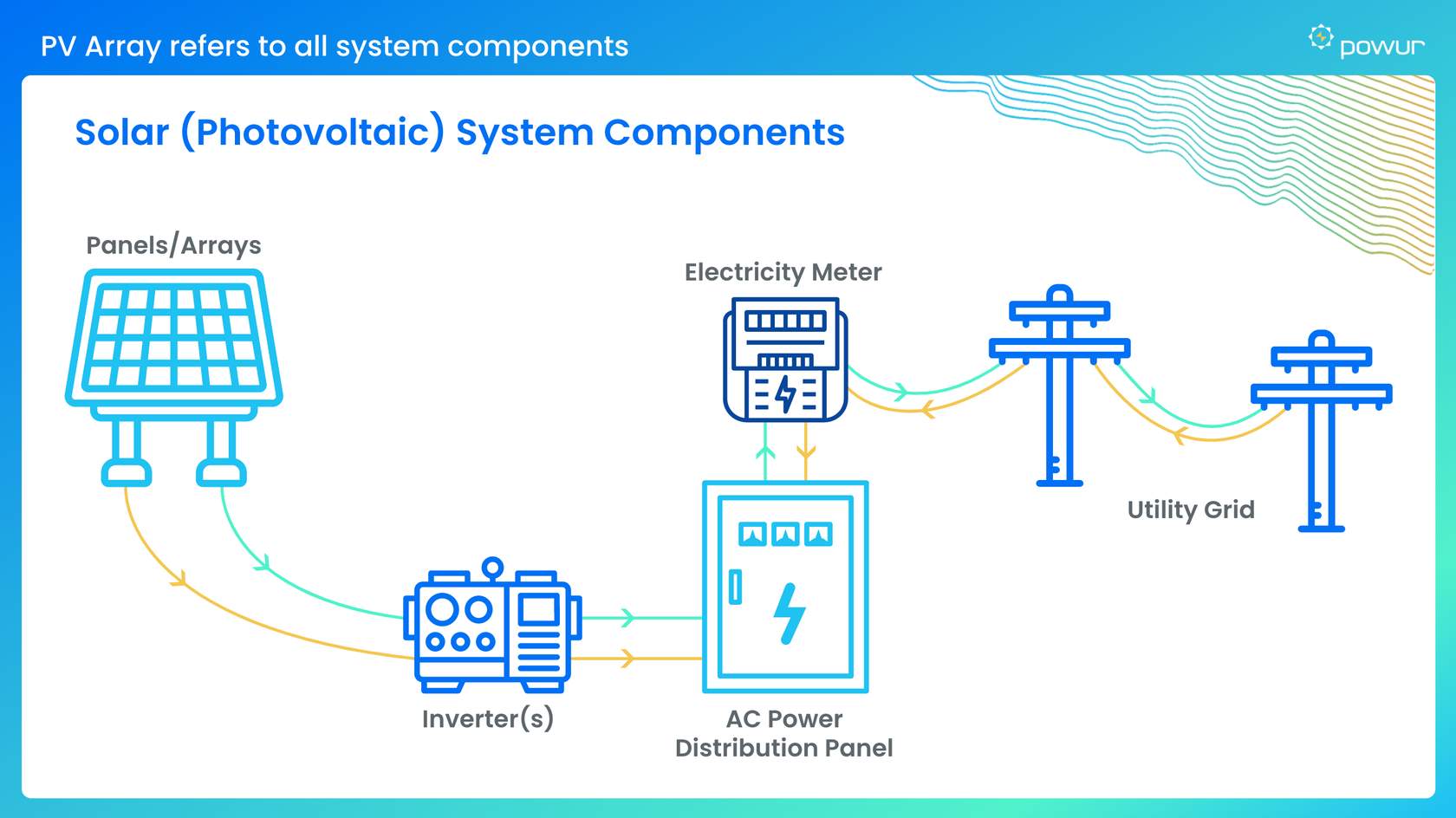
When employing microinverters, all solar panels in an array are wired in parallel. This configuration allows the power generated by each module to be directly channeled to the main electric panel with sufficient Ampacity to supply the home or feed into the grid.
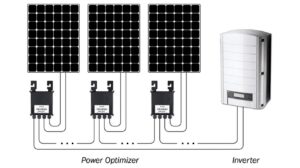
Inverters + Power Optimizers: Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
Understanding Power Optimizers
A Power Optimizer serves as a DC/DC converter that is directly linked to each solar module, effectively transforming them into intelligent components. These Power Optimizers enhance energy output in photovoltaic (PV) systems by continuously monitoring and adjusting each module’s maximum power point (MPPT) individually, while also providing real-time performance data.
Optimized Solution: Independent Panels
This optimized approach empowers solar panels to function autonomously, merging the benefits of a central inverter with the capabilities of microinverters. By incorporating optimizers beneath each module, the system operates in series to compensate for underperforming modules. The neighboring optimizers within the series elevate voltage for modules experiencing reduced output, such as those affected by shading.
Efficiency and Collaboration
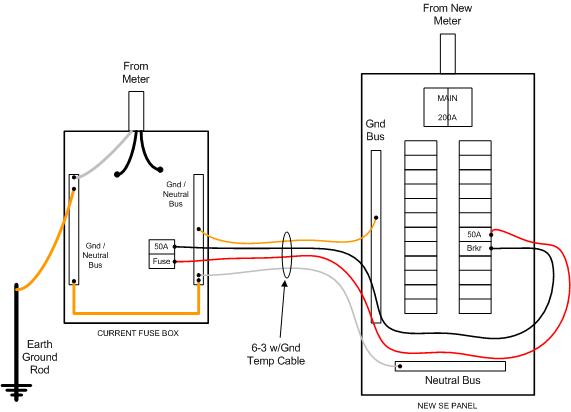
With optimizers positioned on the roof and an inverter located on the wall, energy conversion transpires at a central location. Consequently, this configuration minimizes energy loss and enhances overall efficiency compared to microinverters. Furthermore, optimized inverters require less breaker space in the main service panel. This feature can potentially negate the need for a service panel upgrade, even when incorporating batteries and electric vehicle (EV) chargers. As a result, electrical upgrades become less frequent when adopting this solution.
This amalgamation of inverters and Power Optimizers presents a balanced alternative that delivers improved performance, greater efficiency, and the potential for reduced system complexity. It is important to consult with a solar professional to evaluate whether this solution aligns with your specific requirements and goals.
String Inverters: Simplified Solar Energy Conversion
Introduction to String Inverters
String inverters have been at the forefront of residential inverter technology, particularly during the 2000s and 2010s. This popularity can be attributed to their cost-efficiency and straightforward installation process.
Operation of String Inverters
The operation of string inverters revolves around connecting a “string” of solar panels together, with the possibility of combining multiple strings. The collective power generated by these panels is directed to a central inverter. In essence, the solar panels on the roof produce DC power, which is then channeled to a single inverter located in close proximity to the electric panel.
Cost-Efficiency and Practicality
String inverters are especially well-suited for homeowners who do not have to contend with shading issues and are seeking to manage their project costs. Their uncomplicated design and installation process make them an ideal choice for those prioritizing simplicity and affordability in their solar energy conversion journey.
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Solar System: Microinverters, Power Optimizers, or String Inverters?
Selecting the optimal inverter technology for your solar system involves careful consideration of various factors. Let’s delve into the characteristics of each option to help you make an informed decision.
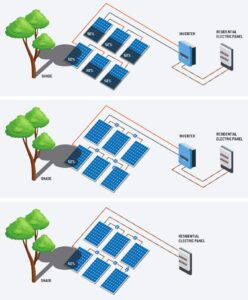
Microinverters: Maximizing Flexibility and Shading Performance
- Flexibility: Microinverters offer the highest level of flexibility as each solar panel operates independently. This is particularly advantageous for panels with varying orientations or shading concerns.
- Shade Tolerance: Microinverters excel in shaded conditions because shading on one panel doesn’t compromise the entire array’s output.
- Warranty: These inverters often come with extended warranties, providing peace of mind for maintenance and repairs.
- Installation: They require less equipment for installation and enable more conventional home wiring methods, simplifying the installation process.
Power Optimizers: Balancing Performance and Shade Mitigation
- Performance: Power optimizers, especially when paired with a central inverter like SolarEdge’s system, can yield higher performance, especially on unshaded and straightforward roof planes.
- Shade Mitigation: These optimizers enhance production and system capabilities even in the presence of shading. They optimize each panel’s output, compensating for shaded panels.
String Inverters: Tradeoffs and Considerations
- While the text doesn’t provide extensive details about string inverters, it hints at tradeoffs in areas such as system expansion, compatibility, reliability, and efficiency. These factors might make them a less popular choice.
Key Considerations for Your Choice
- Shading: If shading is significant, microinverters or power optimizers could be more suitable to ensure optimal panel performance.
- Warranty: Microinverters may be appealing due to their longer warranties, providing added security.
- Cost: Compare the costs of microinverters, power optimizers, and string inverters to align with your budget.
- System Complexity: Evaluate the installation equipment and its impact on overall system complexity.
- Efficiency: Consider the efficiency of each option and its long-term impact on energy production.
- Future Expansion: If future system expansion is planned, opt for the option with the simplest expansion process.
Conclusion: A Tailored Decision
Ultimately, the choice among microinverters, power optimizers, or string inverters depends on your specific priorities and circumstances. To make the best decision, consult solar energy professionals who can analyze your situation and provide personalized recommendations based on your unique needs.