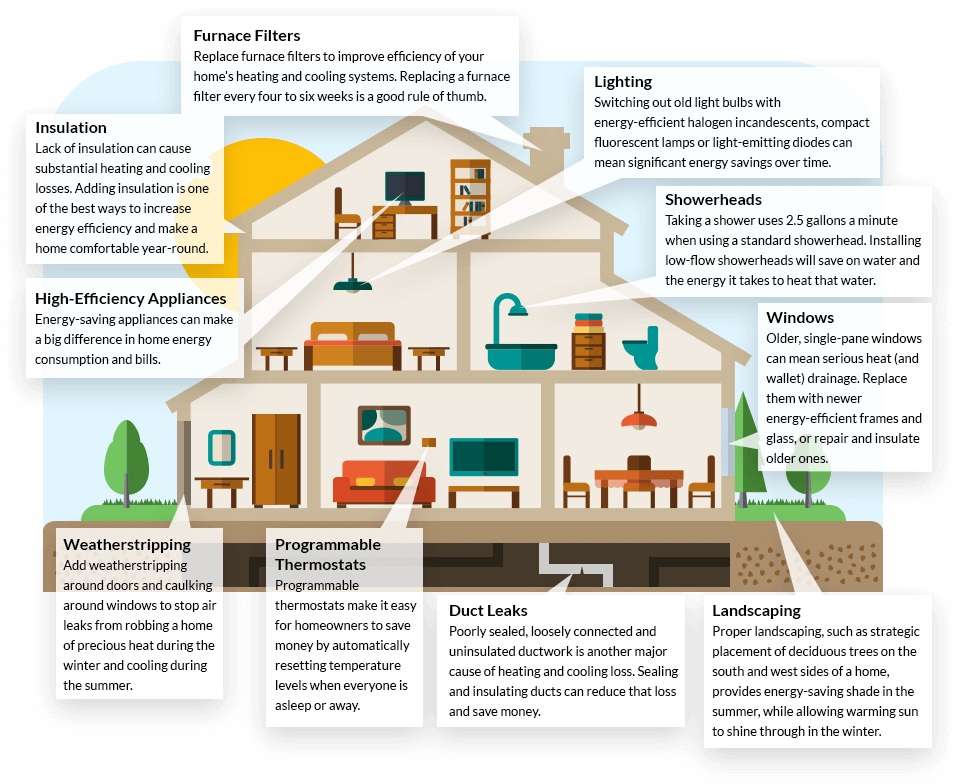
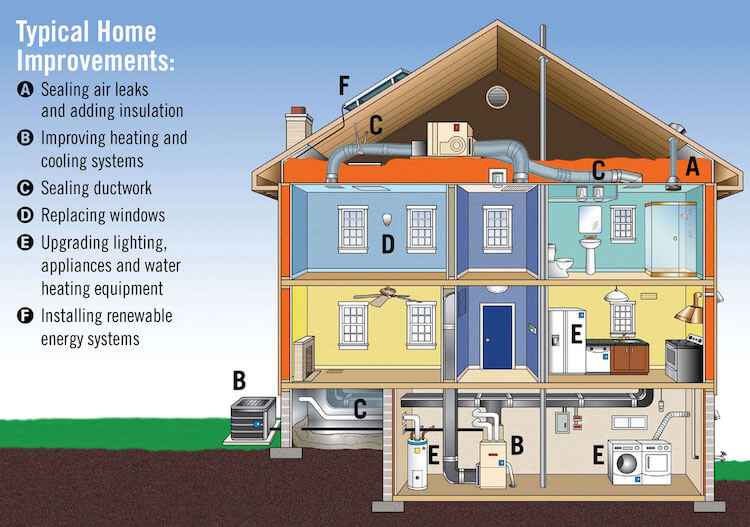
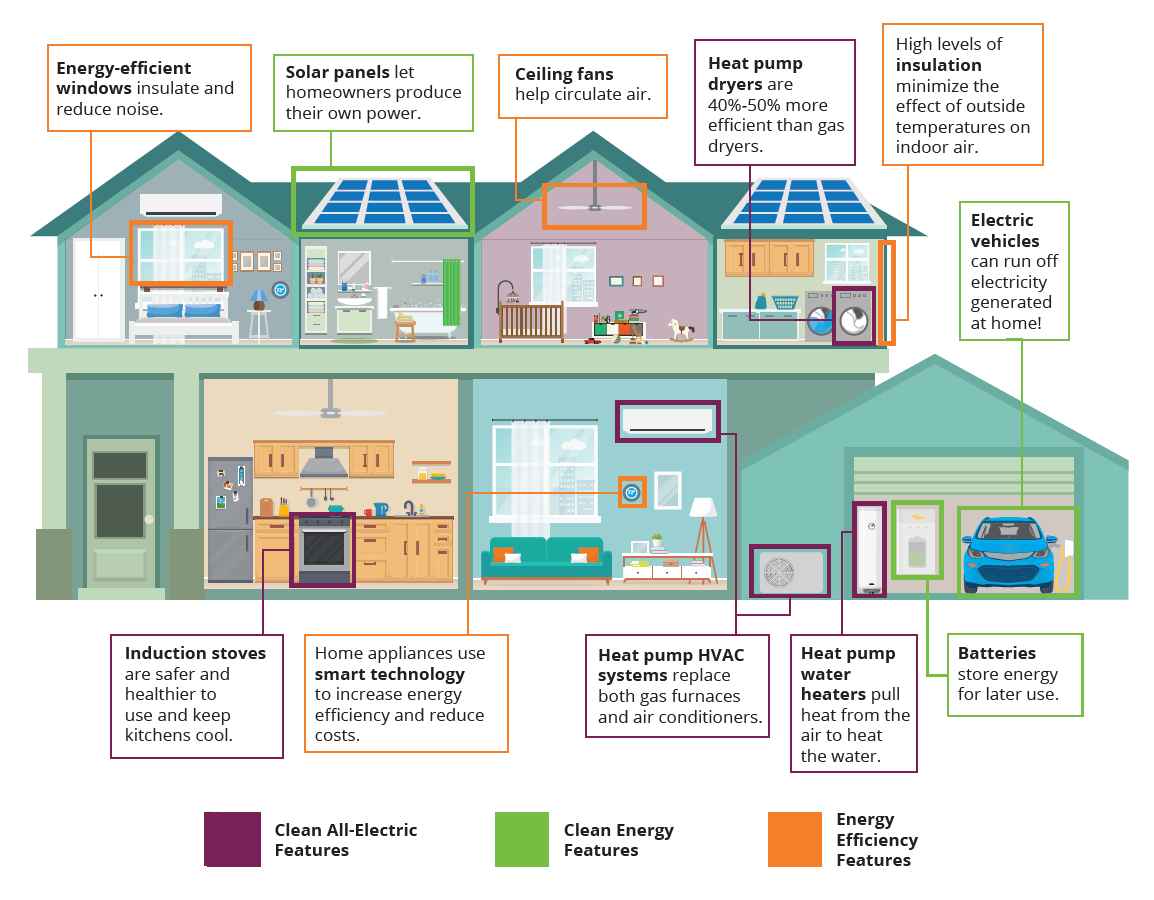
Going solar is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective way to generate electricity for homes. However, choosing the right financial option can significantly impact the overall benefits. Below, we’ll delve into the advantages and disadvantages of various approaches to help determine the optimal financial decision for clients.
1. Paying with Cash
Advantages:
- Economical: Cash purchase is the most cost-effective method, with installation costs ranging from 6 to 8 cents per kWh.
- No Additional Costs: There are no financing fees or interest charges.
- Quick ROI: Typically, a return on investment is achieved within 5-7 years.
- Discounts: Customers can save 20-30% by avoiding financing fees.
- ITC Tax Credit: Homeowners can keep the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) as it’s not used to finance the purchase.
- Ownership: Homeowners own the system outright, producing energy without finance-related fees.
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Payment: Requires a substantial upfront payment.
- Cash Outflow: Immediate cash outflow affects short-term liquidity.
2. Low-Interest Loan
Advantages:
- Affordable: Low monthly payments with flexible loan terms.
- Preserve Cash: Avoids a large upfront payment.
- Locked Energy Costs: Monthly payments secure energy costs over the loan duration.
- Tax Incentives: Homeowners qualify for tax credits and incentives.
Disadvantages:
- Interest Costs: Accrual of interest over the loan term.
- Loan Obligation: Debt obligation for the loan duration.
- Potential Eligibility Issues: Loan approval depends on creditworthiness.
3. Solar Lease
Advantages:
- Zero Down Payment: No upfront payment is required.
- Low Payments: Monthly lease payments are often lower than current electric bills.
- Immediate Savings: Homeowners start saving from the outset.
- Fixed Costs: Stable monthly payments despite rising utility rates.
Disadvantages:
- No Ownership: Homeowners do not own the system.
- Limited Savings: Potential savings capped at 5-50%.
- No Tax Credits: Tax incentives usually go to the leasing company.
4. Power Purchase Agreement (PPA)
Advantages:
- Price Stability: Steady energy prices over the PPA term.
- Lower Monthly Payments: Often lower than existing utility bills.
- Long-Term Savings: Cumulative savings despite escalators.
Disadvantages:
- No Ownership: Homeowners do not own the system.
- Contractual Obligation: Locked into a PPA term.
- Limited Control: Homeowners rely on the solar system provider’s performance.
5. PACE Financing
Advantages:
- No Credit Check: Approval is not based on personal credit.
- Property Value Leveraging: Repayment tied to property taxes.
- Flexible Terms: Repayment terms range from 5 to 30 years.
- $0 Down: No upfront payment is required.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Availability: PACE programs are available in specific markets.
- Property Tax Impact: Increased property tax payments.
- Interest Costs: Incurs interest charges.
6. Loan Payment Structure
- Introductory Phase: Solar loans may have an initial phase with lower payments.
- ITC Utilization: Assumes tax refund equivalent to the 30% ITC.
- Automatic Amortization: Amortization is scheduled after 18 months.
7. Lender Caps and Calculation
- Price per Watt Caps: Lenders limit the loan amount based on system size.
- Adders and Storage: Caps differ based on eligible adders and storage inclusion.
8. Handling Solar Financials During Home Sale
- Solar Loan: Can be paid off or transferred to the new homeowner.
- Solar Lease/PPA: Options for new homeowner assumption or purchase.
9. ITC Guarantee and Loan Considerations
- ITC Dependency: ITC depends on the customer’s tax liability.
- Caution with Promises: Never promise ITC benefits; consult tax professionals.
10. Amortization Loan and FlexPay
- Amortization Loan Increase: Payment increase at month 18, if not on autopay.
- FlexPay: Loan amortization at 18 or 36 months, three payment options.
11. Loan Details and Flexibility
- Fixed APR: 25-year loan at 2.99% APR.
- Payment Structure: Initial payments and optional 30% payment in month 18.
- Estimates: Payment estimates are subject to the loan agreement.
In conclusion, evaluating the pros and cons of each financial alternative helps determine the best fit for clients seeking to go solar. Understanding the unique benefits and drawbacks of cash payment, low-interest loans, leasing, PPAs, PACE financing, and more empowers financial advisors to guide clients toward the optimal decision aligned with their preferences and financial circumstances.