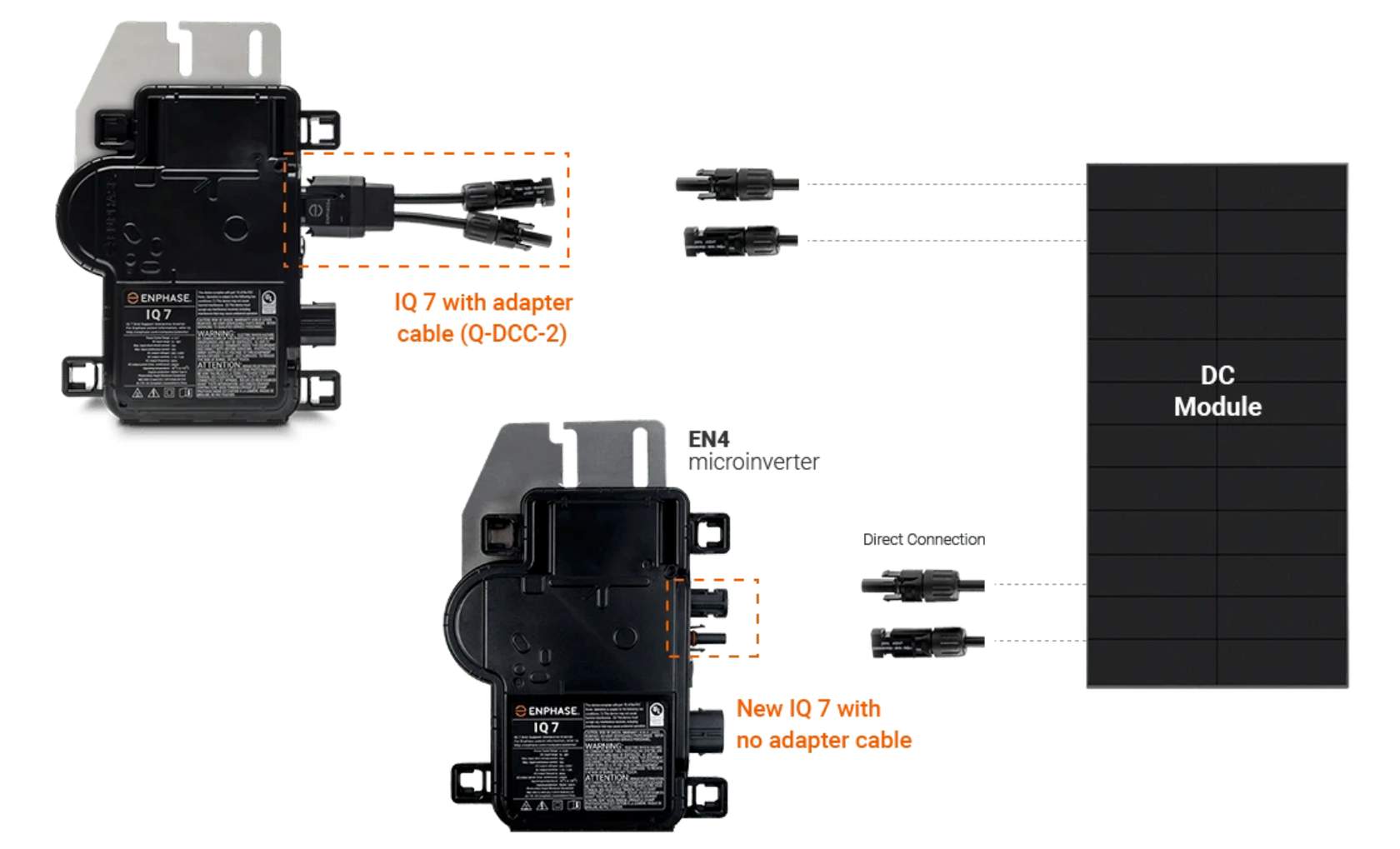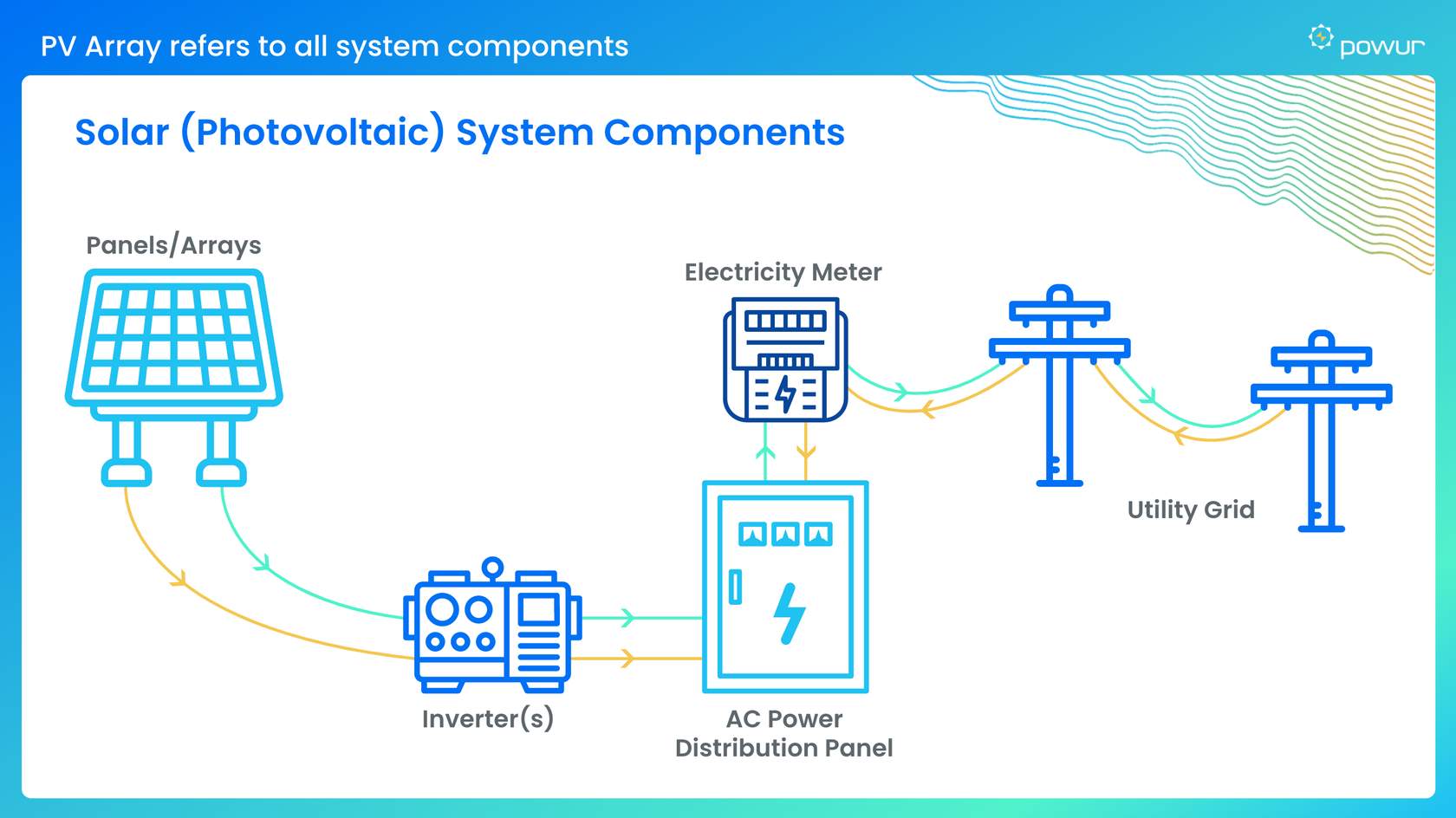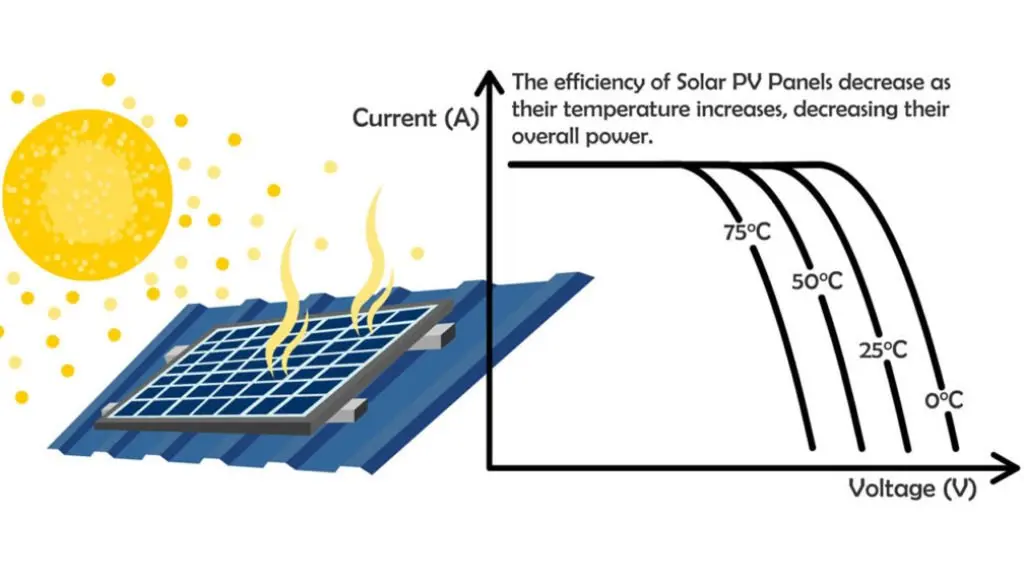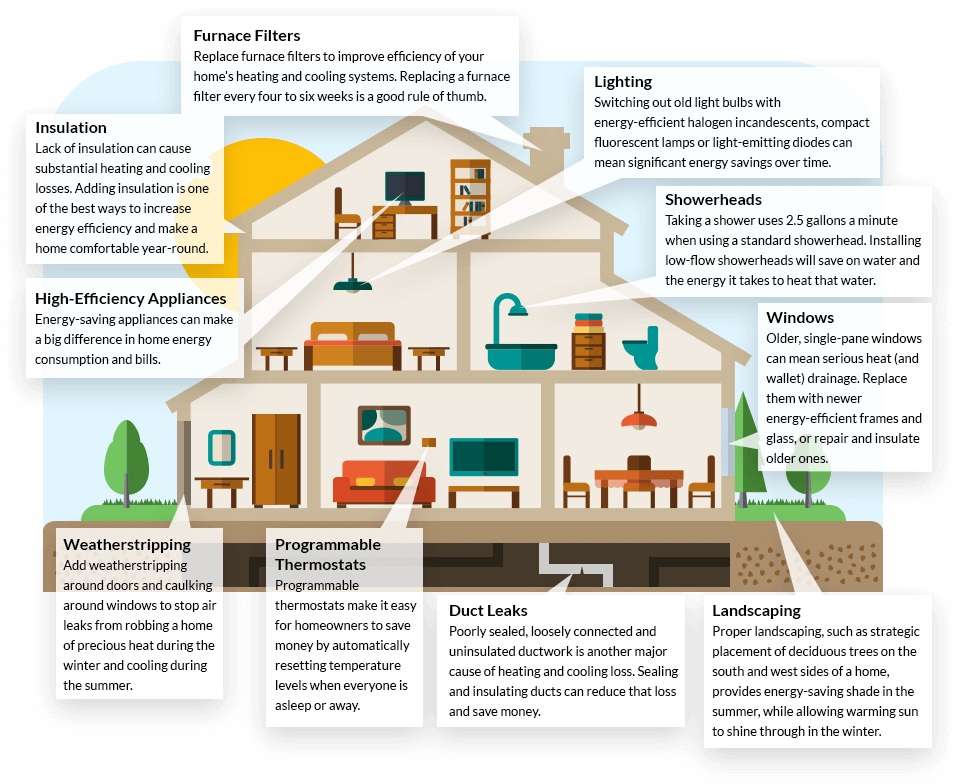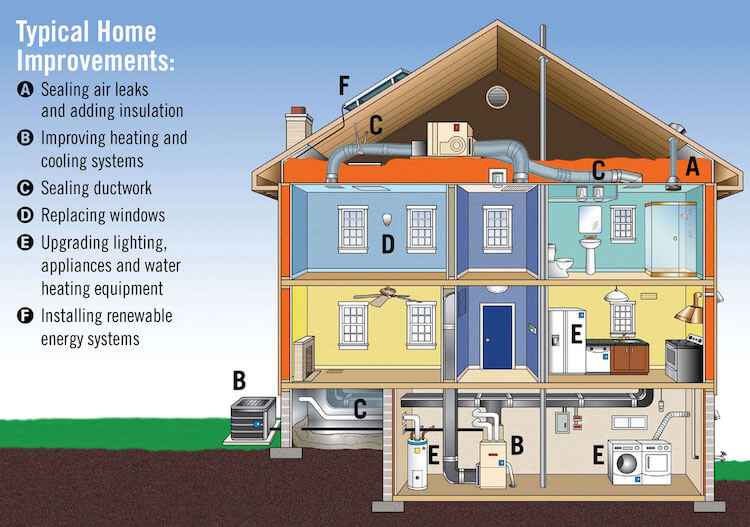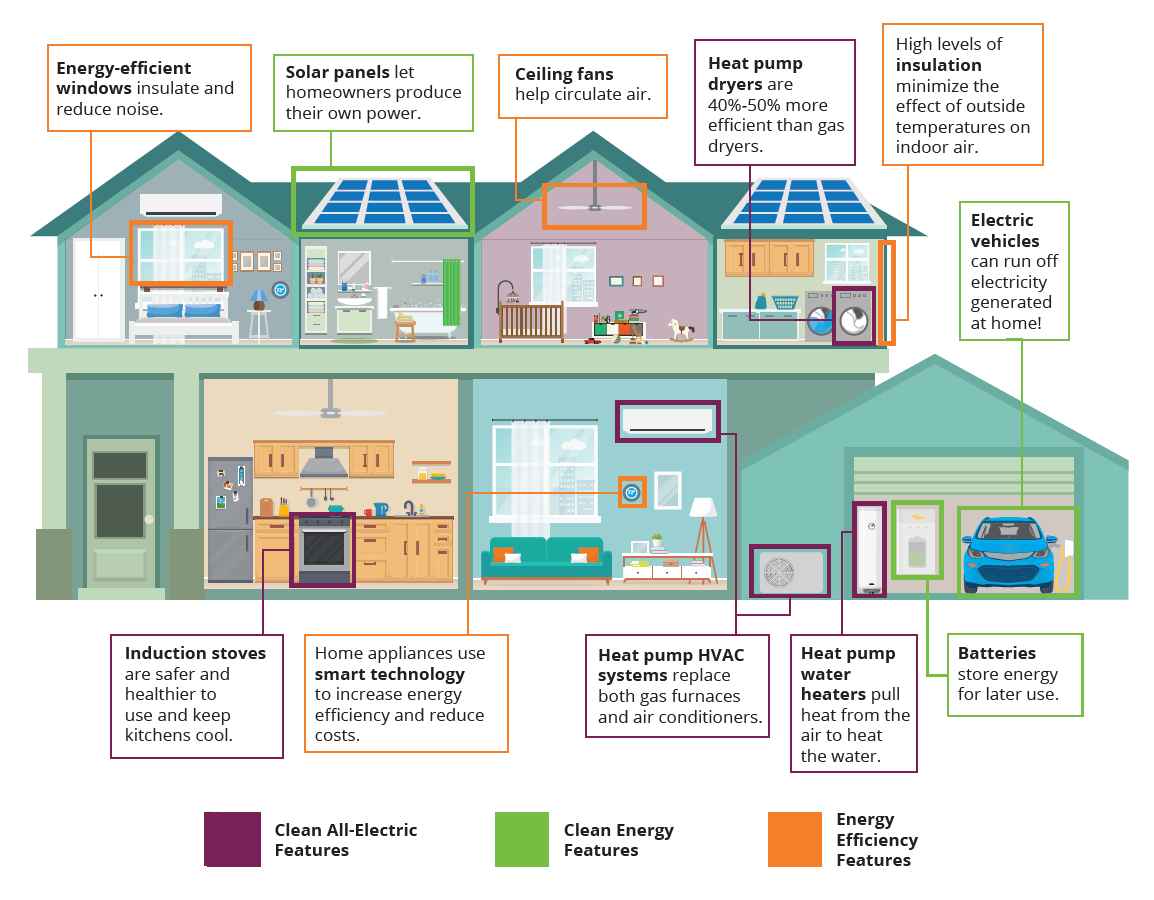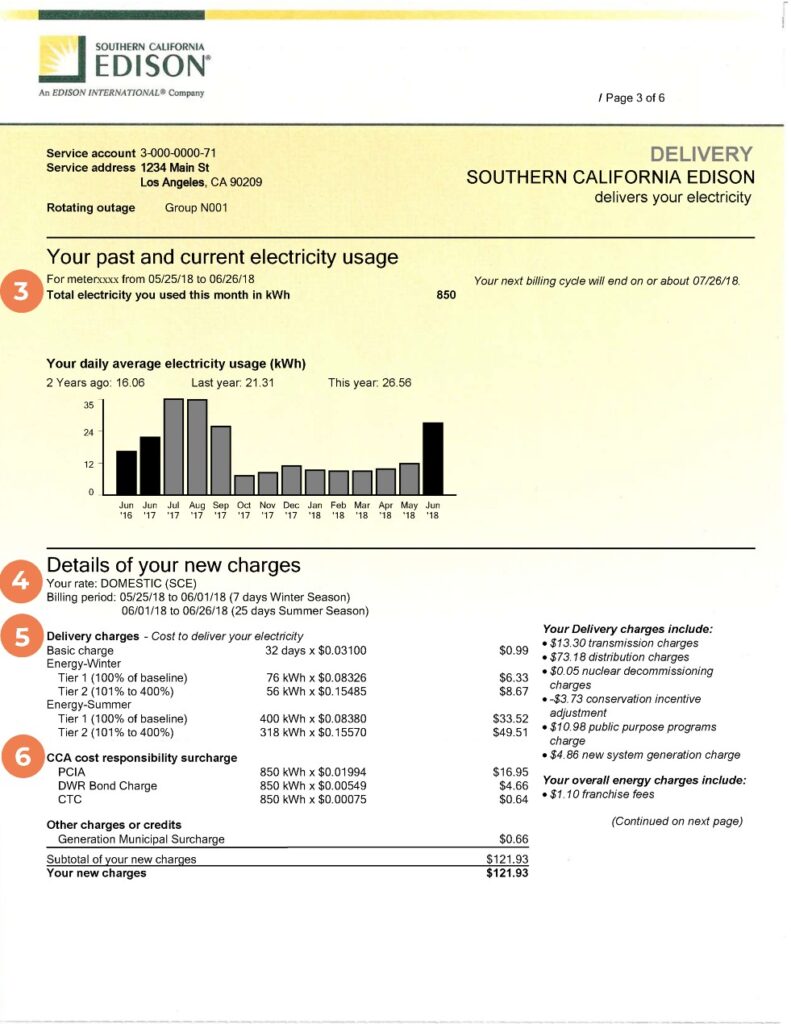
Electric bills exhibit variability due to factors such as location, energy consumption, and local utility practices. While specific charges and terms may differ depending on your area and utility provider, several common components are usually present. These are some typical charges that might appear on your electric bill:
Usage Charges:
- Energy Consumption: This represents the cost for the actual electricity used during the billing period, often measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Demand Charges: For businesses and industries, this fee reflects the highest electricity usage within a specific timeframe (e.g., 15-minute interval) during the billing cycle, indicating stress on the utility’s distribution system.
Delivery Charges:
- Distribution Charges: Cover expenses for maintaining and enhancing the local distribution system responsible for delivering electricity to homes and businesses.
- Transmission Charges: Support the expense of transmitting electricity over high-voltage lines from power plants to local distribution networks.
- Customer Charges: A fixed fee to account for the utility’s fixed costs, including meter reading, billing, customer service, and administrative expenses.
- Service Fees: Include charges for services like reconnecting a disconnected service, changing meters, or installing new equipment.
Supply Charges:
- Generation Charges: Reflect the cost of electricity generation at power plants, encompassing fuel, operation, maintenance, and capital investments.
- Renewable Energy Charges: If your utility offers or requires a renewable energy program, you might see a distinct charge or credit linked to renewable energy sources.
Taxes and Fees:
- Local Taxes: Taxes levied by local governments on electricity consumption.
- State Taxes: State-level taxes or fees linked to electricity usage.
- Franchise Fees: Payments to the local municipality for the privilege of operating within its jurisdiction.
- Regulatory Fees: Fees gathered to support regulatory agencies overseeing the energy sector.
Miscellaneous Charges:
- Late Payment Fees: Applied when bills aren’t paid by the due date.
- Meter Rent/Lease Charges: If you’re leasing your electricity meter from the utility, this fee covers the expense.
- Energy Efficiency Programs: Certain utilities impose a fee to back energy-saving initiatives.
- Nuclear Decommissioning: In areas with nuclear power plants, this fee contributes to the future dismantling and cleanup of those facilities.
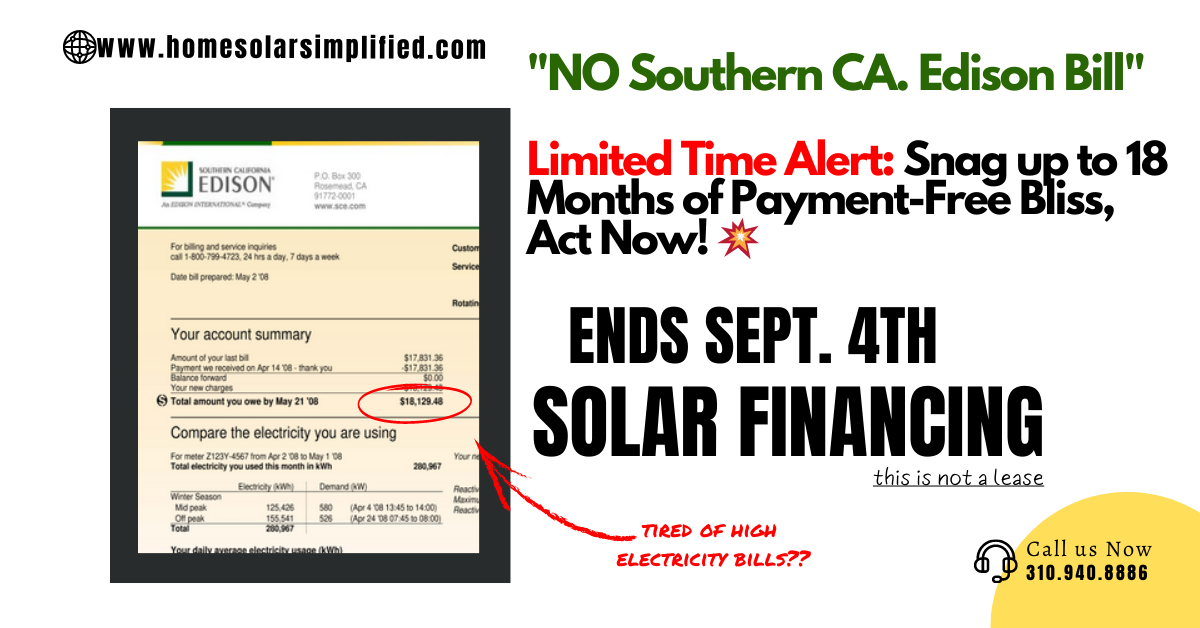
Post-Solar Electric Bill:
A post-solar electric bill showcases the impact of solar adoption on charges. By generating their electricity through solar panels, customers reduce their reliance on utility supply and lower their need for delivery. The intricacies of electric bills are essential for meaningful solar discussions. It allows customers to understand their current charges, perceive the effects of increasing rates, and recognize the potential of mitigating utility expenses through solar integration. Remember that bill details can vary, so reviewing your bill carefully and seeking clarification from your utility’s customer service is advisable.