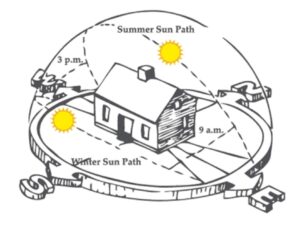
In this depiction, it is clear that the path of the Sun shifts over the course of the year, leading to varying Solar Access between the summer and winter seasons. As a result, it is recommended to consider the average Solar Access across all seasons.
Even though your client’s home might experience abundant sunlight in July and August when the Sun is directly overhead, there could be a reduction in energy generation during other months. It is crucial to carefully evaluate these factors when making decisions.
Thoroughly scrutinize all obstructions, irrespective of their size.
Shading issues aren’t exclusively the result of trees, chimneys, and dormers.
In this case, shading generated by a utility pole is affecting multiple solar panels in this arrangement. Despite only a limited portion of solar cells being shaded across a handful of modules, this can substantially reduce production and, in certain instances, completely stop panel output.
Inspect the neighboring structures as well.
When roofs are positioned at different heights or when there are adjacent buildings close to the proposed solar roof, these features or other parts of the roof might cause problems with shading.
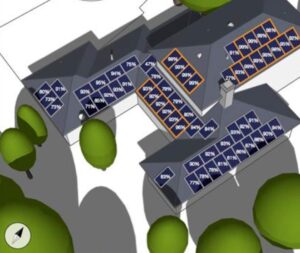
Consider the changing patterns of shade throughout the day and the year. The image provided illustrates that approximately 20% of the panels on this roof will encounter significant shading because of nearby structures.
Examine potential chimney blockages.
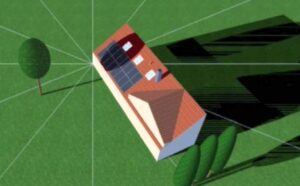
In the image provided, the distinct outline cast by the shadow of a chimney is evident. During the system planning phase, there is an opportunity to tactically place panels to reduce shading caused by obstacles, much like the method demonstrated in this scenario. The panels have been organized in a way that diminishes the influence of shading stemming from this chimney.
Utilize creative panel placement techniques
In this case, even with shading affecting the roof’s southern exposure, the panels have been cleverly placed to mitigate its effects.
When there is abundant space to work with, considering innovative panel positioning can result in a more productive system and potentially eliminate the need for customers to incur costs related to tree trimming or removal.
Consider all periods of the day and year
Remember that the time of day and the season can both contribute to shading problems caused by trees, even if those trees don’t appear to be problematic initially.
Consider the combined effect of all factors.
The provided image showcases the anticipated solar panel output, demonstrating that production is affected not only by shading but also by orientation aspects like pitch and azimuth. It’s crucial to acknowledge that solar accessibility encompasses considerations beyond just shading.
In conclusion, Solar Access assumes a pivotal role in the realm of solar energy production, with shading standing out as the principal determinant for achieving optimal outcomes. Shading significantly governs the extent of solar energy reaching a panel throughout each day, month, year, and the project’s lifespan, thereby impacting its potential for power generation. When assessing a residence’s suitability for solar installation, it’s imperative to consider not only evident obstructions like trees, but also the dynamic shifts in sun angles over the seasons, which can render seemingly minor elements such as chimneys, utility poles, or distant mountains substantial in their impact. Leveraging perceptive observation skills and insights into shading is key to devising effective systems and conveying their effects lucidly. Essentially, scrupulous planning and astute observation stand as critical cornerstones for judiciously siting solar panels, elevating energy yield, and mitigating the necessity for costly tree pruning or structural modifications.